Gallery:




















The Race:
Celebrating its 10th Anniversary this year, The The Canadian Death Race is widely regarded as the toughest ultramarathon (any running race longer than the traditional 42.2 km marathon) in Canada. Located in the small rocky mountain town of Grande Cache Alberta, this race course covers requires athletes to cover 125 km and summit 3 mountains (total elevation gain of 17,000 feet) in under 24 hours. Despite this daunting challenge, 1500 racers (solo and teams) annually compete to test their abilities on this unrelenting and unpredictable race course.
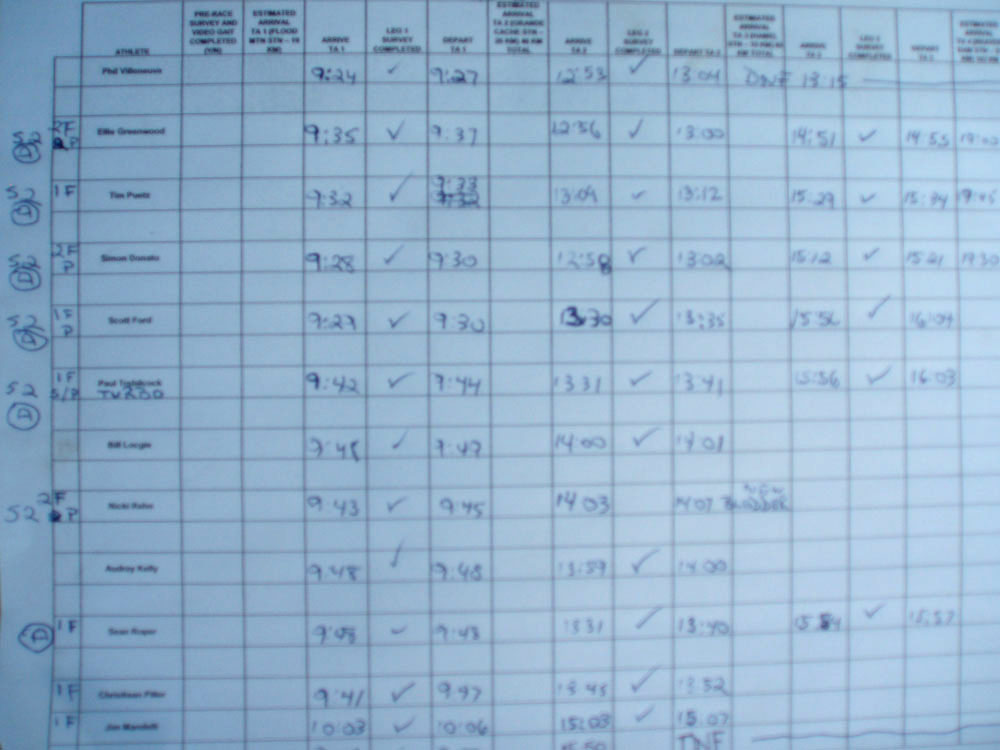
This year, Adventure Science has teamed up with 15 highly trained endurance athletes and ultra runners to test themselves by racing solo on the race course. The athletes will also be participating in a study to analyze running biomechanics and the role of core strength in the maintenance of running gait.
The race organizers note on their website this race is not about the prizes, it's about the glory :“There are no big prizes for winning: finishing is hard enough. And the bragging rights are priceless.”Right now the glory is held by Jack Cook (Edmonton Canada) and Lisa Polizzi (Brisbane Australia) who both set the male and female course records in 2006 at 13:48:24 and 14:20:27. Will these records survive 2010?
The Race Course:
Race course maps used with permission/courtesy of and © Canadian Institute of Extreme Racing.
Downloadable .pdf versions are available through the Canadian Death Race Brochure.
Study on Biomechanics:
Background:
The biomechanics (the way our muscles, tendons, ligaments, and bones work to produce movement) of running has been long studied by running coaches and researchers, all looking for the perfect technique that will make runners faster and less prone to injury. Recently, there has been a great deal of both media and scientific attention focused on the biomechanics of barefoot running, and the potential benefits it provides to injury avoidance. This is due, in part, to a renewed examination of the startling injury statistics that exist amongst shoe wearing runners. Proponents of barefoot running suggest that in addition to the running gait changing (landing forefoot and midfoot vs. heel striking), there is also an overall strengthening of the foot (arch in particular) and lower leg muscles, which is thought to help reduce running injuries such as plantar fasciitis, shin splints, a variety of knee injuries, etc.
Rarely in science do we observe a simple cause and effect scenario in complex systems such as the human body (for example shoes = injury and no shoes = no injury). Instead, we typically see several factors working together to produce the outcome. Ultimately, since the biomechanics of running incorporate the entire body, and not just the legs, we are interested in learning how the body responds when running biomechanics break down over time and distance. The Canadian Death Race provides the perfect venue for this with it's physically challenging terrain and course length. Our study group is composed of 15 highly trained endurance athletes who have all been running and racing for over 5 years.
Hypothesis and Study:
As the athletes become fatigued during this race, their running form (biomechanics) will begin to change. As their running form changes, we expect the prevalence of discomfort, pain, and potentially injury to increase. Therefore the maintenance of good running biomechanics may slow or prevent discomfort, pain, and injury over long distances or continuous hours of running.We have identified the core muscles as critical to the maintenance of good running form and suggest that a strong core should allow an athlete to maintain their “natural” running form longer than athletes with a weaker core. This may result in a lower incidence of discomfort, pain, and injury in athletes with stronger core muscles.
To test this we have divided the adventure science athletes into two groups. One group was provided a 16-week core training program specifically designed to 1) teach them to activate and properly contract their core muscles, 2) strengthen their core muscles specifically for running. The other group will continue to train and prepare for this race as they normally would for a competition, without modifying any endurance or strength workouts. Before, during, and after the race all Adventure Science athletes will be filmed in order to analyze changes in their running gait. The athletes will also be surveyed before, during, and after the race to collect data on fatigue level, pain and discomfort perception.
Questions to Answer:
- How does a runner's gait change over distance? Does this differ between the two sample sets?
- Is there a common distance or time at which a running gait begins to deteriorate amongst trained endurance athletes? Does this vary between the two sample sets?
- What is the progression in the perception of discomfort to injury amongst the athletes, and does this differ between the two sample sets?
- Are the athletes who followed the specified core strengthening program able to maintain their “natural” running gait longer than those who did not?
- Did the athletes who followed the specified core strengthening program experience less discomfort, pain, and injury than those who did not?
Results: “Go Death Racer”, Simon’s CDR recap
Adventure Science thanks its sponsors:
Interested in sponsoring Adventure Science? Contact us to find out how!






















